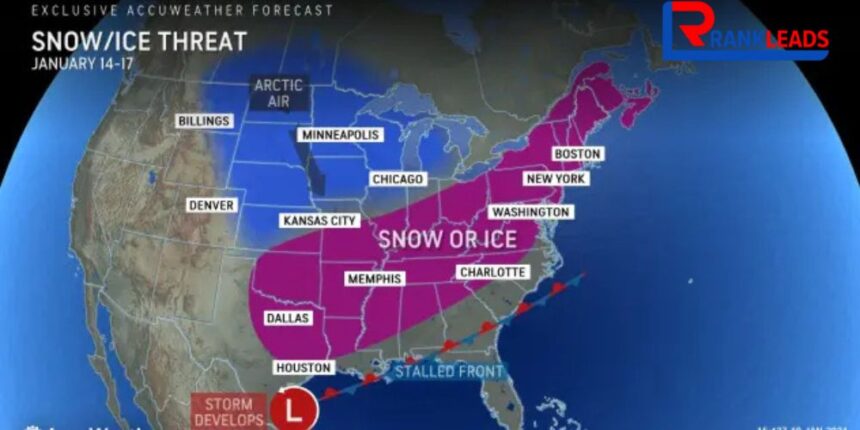
progresses, the United States is experiencing another blast of Arctic air. This surge of frigid temperatures is impacting a large portion of the central US, leaving many wondering about the causes of these extreme cold conditions. A critical question that often arises in these scenarios is whether the cold outbreak is linked to the polar vortex. In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind the Arctic blast of 2024, examining the polar vortex, atmospheric dynamics, and the interplay of various meteorological factors that contribute to such cold weather events.
What is an Arctic Blast?
An Arctic blast refers to a mass of extremely cold air that originates from the Arctic region and moves southward into areas typically not accustomed to such low temperatures. These air masses are characterized by very cold temperatures, often accompanied by harsh winds and significant temperature drops. The term “Arctic blast” is commonly used when these frigid conditions affect a wide region, causing discomfort, potential hazards, and disruptions.
While Arctic blasts can happen throughout the winter, their intensity and duration can vary. In 2024, a strong Arctic blast made its way across the central US, bringing bone-chilling temperatures and frosty conditions. To understand the science behind this event, we need to explore the polar vortex and other atmospheric mechanisms at play.
The Role of the Polar Vortex in Arctic Air Outbreaks
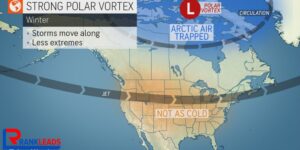
What is the Polar Vortex?
The polar vortex is a large, rotating mass of cold air located in the upper levels of the atmosphere near the North Pole. It is a semi-permanent feature of the winter weather system that helps contain frigid Arctic air within the polar region. When the polar vortex is strong, it remains centered around the pole, and the colder air stays trapped in the Arctic. In this scenario, regions like Europe, Asia, and the eastern US tend to experience milder winter conditions.
However, when the polar vortex weakens or stretches, it can become unstable and send surges of cold air southward into lower latitudes. This is when Arctic blasts are most likely to occur. The vortex can either shift or stretch out, affecting the jet stream and allowing cold air to spill over the northern continents.
Polar Vortex Behavior in 2024
In January 2024, the polar vortex was stronger than usual, with winds around the 60N latitude remaining above average. This strength is usually associated with warmer temperatures across Europe and Asia due to the northward shift of the jet stream. However, in the United States, the situation was different. Despite a stronger-than-average polar vortex, cold air was still able to spill into the central US. This discrepancy led meteorologists to examine other factors contributing to the cold weather.
One critical factor was the stretching of the polar vortex. In contrast to previous cold air outbreaks, where the vortex remained centered over Asia, the vortex in January 2024 stretched across Canada and Hudson Bay. This stretching was linked to a southward shift of the jet stream, which allowed Arctic air to flow into the continental US.
The Connection Between the Jet Stream and Arctic Air
What is the Jet Stream?
The jet stream is a narrow band of strong winds high in the atmosphere that flows from west to east. It plays a crucial role in shaping weather patterns across the Northern Hemisphere. The position and strength of the jet stream can determine the movement of air masses, including cold Arctic air.
Typically, when the jet stream is positioned to the north, it keeps the cold Arctic air confined to the polar region. However, when the jet stream dips southward (creating a trough), it allows cold air to move into the central US, leading to Arctic outbreaks.
How the Jet Stream Impacts the 2024 Arctic Blast
In January 2024, a strong ridge of high pressure built up near Alaska, which played a significant role in driving the jet stream southward. This dip in the jet stream allowed the cold air from the Arctic to surge into the continental US, creating the intense cold conditions associated with the Arctic blast.
Meteorologists often refer to this atmospheric pattern as a “trough” — a downward dip in the jet stream that enables the transport of cold air. This trough, in combination with the stretched polar vortex, helped fuel the cold outbreak in the central US.
Other Meteorological Factors Contributing to the Arctic Blast

While the polar vortex and jet stream are the primary factors in determining cold air outbreaks, other elements of the atmosphere also play a role. One key factor in the January 2024 Arctic blast was the high-pressure ridge over Alaska. This high-pressure system helped to force the jet stream southward, intensifying the cold air surge.
High-Pressure Systems and Cold Air Surges
A high-pressure system over Alaska, also known as an “Alaskan ridge,” is an atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when warm air aloft causes the air pressure to rise. This can lead to an increase in atmospheric stability and cause the jet stream to dip southward. When the jet stream is forced downward, it pulls cold Arctic air into the US, leading to a significant temperature drop.
In the case of the 2024 Arctic blast, the strong Alaskan ridge played a key role in driving the cold air from the polar region into the continental US. This was an important factor that helped enhance the Arctic blast, even though the polar vortex was already stretched and active.
The Impact of the 2024 Arctic Blast on the US
Temperature Drops Across the Central US
The Arctic blast of 2024 caused significant temperature drops across the central US. Cities that typically experience milder winters, such as Chicago, St. Louis, and Kansas City, saw sharp declines in temperature. The cold air pushed temperatures well below freezing, with wind chills making it feel even colder.
The blast also caused widespread disruptions, including flight delays, power outages, and hazardous road conditions. In some areas, temperatures plummeted to well below zero, breaking previous records for the coldest temperatures in January.
The Effect on the Eastern US and Europe
While the central US experienced a dramatic cold snap, other regions felt the effects of the Arctic blast differently. The eastern US saw cooler-than-average temperatures, but it did not experience the extreme cold that affected the Midwest. In contrast, Europe and Asia remained largely unaffected by the cold outbreak, as the strong polar vortex shifted northward, leading to milder-than-average temperatures in those areas.
Can We Predict Future Arctic Blasts?
Predicting Arctic blasts is a challenging task for meteorologists, as many factors come into play, including the behavior of the polar vortex, the jet stream, and high-pressure systems. While scientists have made significant advances in understanding these processes, the exact timing and intensity of cold air outbreaks remain difficult to forecast with certainty.
Meteorologists rely on advanced weather models and observations of atmospheric conditions to predict the likelihood of Arctic blasts. These models use data from satellites, weather stations, and other sources to track the movement of air masses and atmospheric pressure systems. By analyzing these patterns, scientists can provide forecasts and warnings for upcoming cold weather events.
Conclusion: Understanding the Arctic Blast of 202
Though meteorologists have made great strides in understanding the behavior of the polar vortex and its connection to Arctic blasts, there is still much to learn about the underlying dynamics that cause these cold weather events. As climate science advances, we can expect more accurate predictions and better preparation for future Arctic outbreaks, ensuring that communities are ready to face the chill when it arrives.
Understanding the science behind Arctic blasts is essential for adapting to changing weather patterns and mitigating the impacts of extreme cold. By staying informed and prepared, we can better navigate the challenges of winter 2024 and beyond.
Key Takeaways:
- An Arctic blast occurs when extremely cold air from the Arctic region moves southward, affecting regions not typically exposed to such cold temperatures.
- The polar vortex, a rotating mass of cold air near the North Pole, plays a key role in Arctic air outbreaks, but other factors like the jet stream and high-pressure systems are also important contributors.
- In 2024, the stretched polar vortex and the southward dip in the jet stream were major contributors to the cold blast across the US.
- While the polar vortex was strong, other meteorological factors, including the Alaskan ridge, intensified the cold air surge.
- Understanding the dynamics of Arctic blasts can help improve weather predictions and preparedness for extreme cold events in the future.
By grasping the science behind these cold weather events, we can better prepare for the Arctic blasts of the future and minimize their impacts on our daily lives.